

Air pollution exposure affects FEV 1 in asthmatics, but also affects FVC and FEV 1 in healthy adults even at low concentrations. Lung function development is reduced in children who grow up near motorways although this seems at least in part reversible. (In normal individuals, carbon dioxide is the primary determinant of respiratory drive.) the Andes Denver, Colorado Tibet the Himalayas) that person can develop a condition called altitude sickness because their lungs remove adequate amounts of carbon dioxide but they do not take in enough oxygen. When someone living at or near sea level travels to locations at high altitudes (e.g. Also, due to the lower environmental air pressure at higher altitudes, the air pressure within the breathing system must be lower in order to inhale in order to meet this requirement, the thoracic diaphragm has a tendency to lower to a greater extent during inhalation, which in turn causes an increase in lung volume. In response to higher altitude, the body's diffusing capacity increases in order to process more air. This is because the partial pressure of oxygen is lower at higher altitude which, as a result means that oxygen less readily diffuses into the bloodstream. Lung volumes vary with different people as follows:Ī person who is born and lives at sea level will develop a slightly smaller lung capacity than a person who spends their life at a high altitude. Several factors affect lung volumes some can be controlled, and some cannot be controlled. The average human respiratory rate is 30–60 breaths per minute at birth, decreasing to 12–20 breaths per minute in adults. Tidal breathing is normal, resting breathing the tidal volume is the volume of air that is inhaled or exhaled in only a single such breath. The average total lung capacity of an adult human male is about 6 litres of air. Lung volumes and lung capacities refer to the volume of air in the lungs at different phases of the respiratory cycle. Maximal voluntary ventilation: volume of air expired in a specified period during repetitive maximal effort Peak expiratory flow: The highest forced expiratory flow measured with a peak flow meter Unless otherwise specified, volume qualifiers indicate the volume inspired from RV at the point of measurement.) For example, maximum inspiratory flow is denoted FIF max. The maximum instantaneous flow achieved during a FVC maneuverįorced inspiratory flow: (Specific measurement of the forced inspiratory curve is denoted by nomenclature analogous to that for the forced expiratory curve. Volume that has been exhaled at the end of the first second of forced expirationįorced expiratory flow related to some portion of the FVC curve modifiers refer to amount of FVC already exhaled Residual volume expressed as percent of TLCĪctual volume of the lung including the volume of the conducting airway.įorced vital capacity: the determination of the vital capacity from a maximally forced expiratory effortįorced expiratory volume (time): a generic term indicating the volume of air exhaled under forced conditions in the first t seconds
Functional residual capacity tv#
Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during quiet breathing (VT indicates a subdivision of the lung when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol TV or V T is used.)įunctional residual capacity: the volume in the lungs at the end-expiratory position
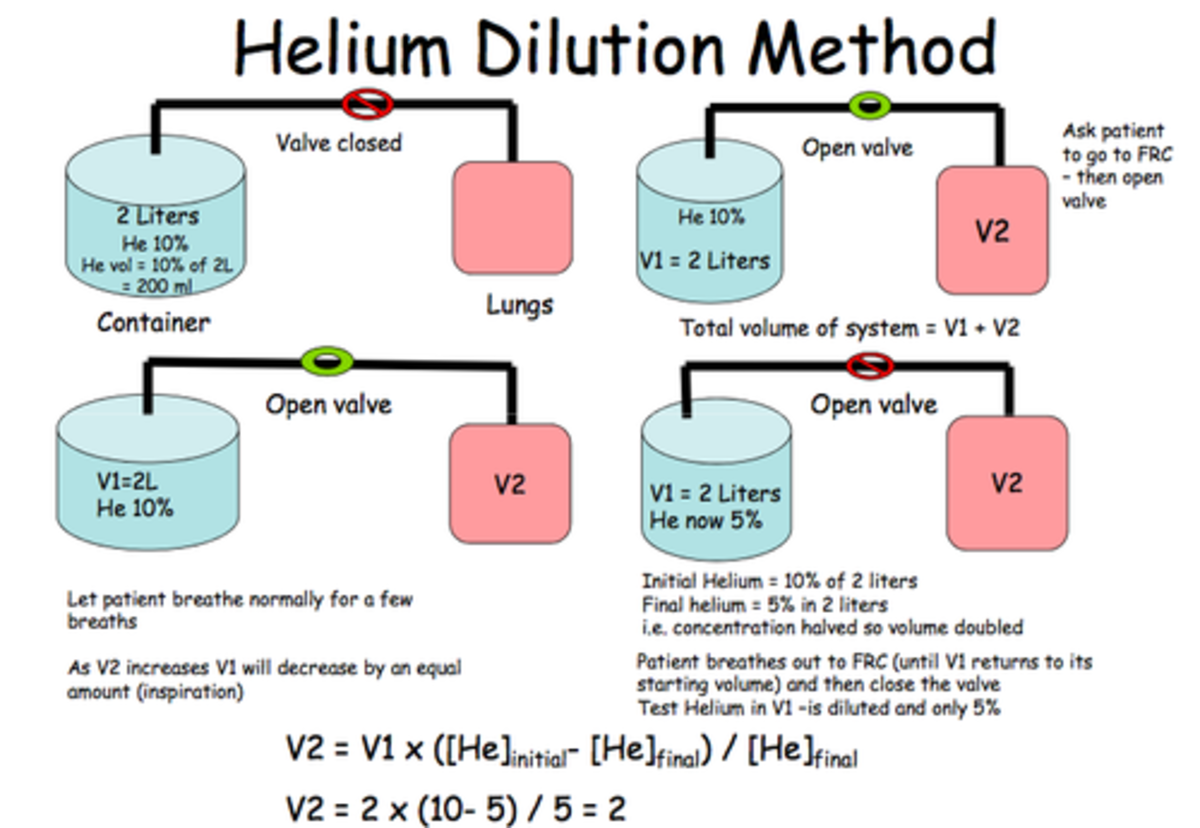
Vital capacity: the volume of air breathed out after the deepest inhalation. Inspiratory vital capacity: the maximum volume of air inhaled from the point of maximum expiration Inspiratory capacity: the sum of IRV and TV Inspiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume that can be inhaled from the end-inspiratory level Residual volume: the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal exhalationĮxpiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume of air that can be exhaled from the end-expiratory position Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during quiet breathing (TV indicates a subdivision of the lung when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol TV or V T is used.) Total lung capacity: the volume in the lungs at maximal inflation, the sum of VC and RV.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
